Introduction
This is the Quaestor User's Guide home page.
Quaestor is a software framework to both develop and use knowledge bases containing computational methods and data. The combination of a project (a project file), a knowledge base (a knowledge file) and the Quaestor program makes a knowledge-based system to streamline design and engineering processes (workflows).
This user documentation is primarily targeted on the use of Quaestor as the development platform for knowledge based engineering. Although this information is also very interesting for users (Domain experts and End-Users), they should primarily rely on the documentation provided inside the knowledge based system or provided separately as a "Getting started" documentation.
Version information can be found in here.
What is Quaestor
Quaestor is a software framework for developing and using knowledge based systems containing computational methods and data. With these systems, you are able to streamline analysis, design and engineering processes.
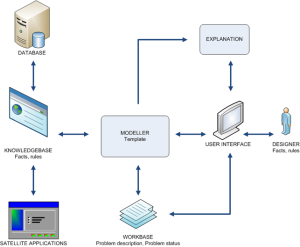
The general architecture can be sketched as follows:
The combination of a project (a project file), a knowledge base (a knowledge file) and the Quaestor program makes a knowledge-based system to streamline design and engineering processes (workflows).
Advantages
Knowledge-based systems in Quaestor enable research, engineering and design departments to simplify the tasks of:
- managing computational methods and model fragments;
- manage and use of complex (and knowledge based) workflows in addition to data and calculation management;
- controlling analysis, design and engineering processes;
- performing goal driven design, engineering and mathematical model development;
- project administration (all information from project data to calculation results and reports in one environment).
Next to the above features, Quaestor provides a flexible computational environment that allows:
- the concurrent use of various computational models (formulas; rules; programs; spreadsheets);
- computing solutions for problems with one or more varying independent parameters;
- easy maintenance and rapid development of new applications by including new model fragments in a knowledge base;
- the use of legacy software, prediction tools, databases, spreadsheets and relations.
This makes Quaestor one of the most powerful environments currently available for the development and use of knowledge-based computational models, applications and configurators.