Page History
...
Simply create a new knowledge base with the following relations:
Couple the QuadraticCurve object the QuadraticCurve object to the relation Y = X^2 through the Constraint Connect menu option in the Knowledge browser:
...
This makes that Y = X^2 is only valid within an instance of QuadraticCurveof QuadraticCurve.
Enter the next relation:
Select Y as top goal and enter a value 3.5 for X. You will see that the QuadraticCurve object the QuadraticCurve object is created in the solution and you will get a result of 12.25.
Enter an additional relation that selects the third Y value from the QuadraticCurve objectthe QuadraticCurve object:
Select Y_3 as top goal will yield a result of 4.0.
...
Introduce into an empty Quaestor the relations:
Connect this relation to the QuadraticCurve object the QuadraticCurve object as is done above.
X must be provided with the @LOCAL attribute in its dataset, since it is to be used both in the solution top level and in the QuadraticCurve levelthe QuadraticCurve level.
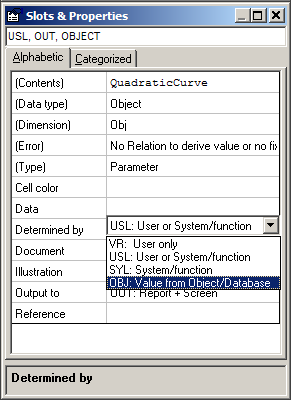
QuadraticCurve must QuadraticCurve must be provided with the OBJ attribute in the Determined By property:
In this case QuadraticCurve is case QuadraticCurve is introduced in the model by the first relation. And the OBJ attribute makes it into a non-computable object which will create the X and Y values through the @X and @Y arguments in the relation (the @ stands for parameter presence in the object).
If you ask for Y and give respectively X=6 (in the solution level) and X=1(1)10 (in the QuadraticCurve level) you will get the obvious result of 36.
...