Page History
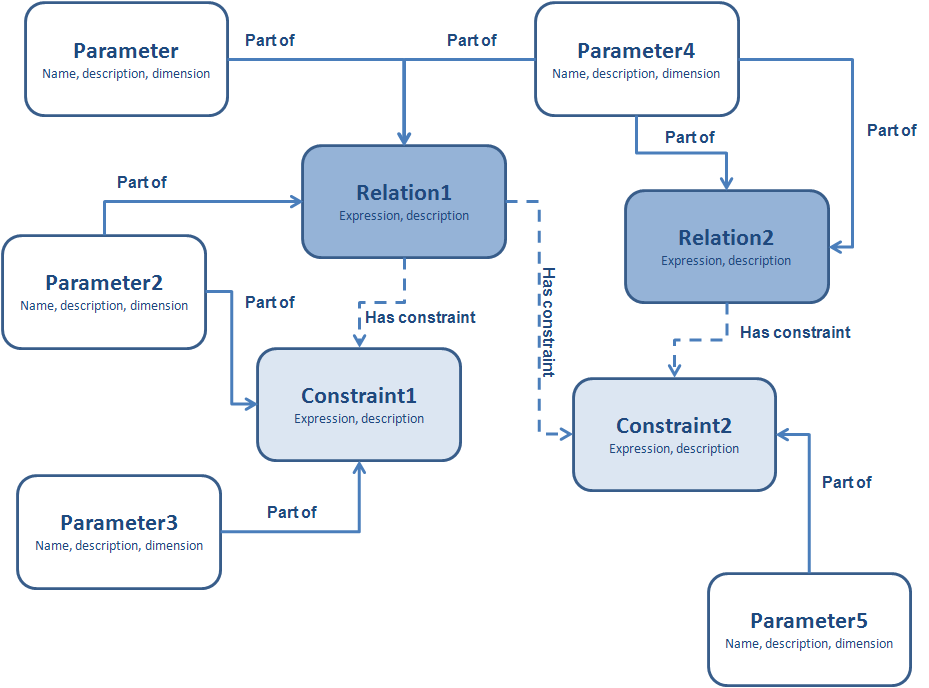
The traditional knowledge domain of Quaestor is a semantic network of frames containing Relations, parameters and Constraint (see figure).
A frame is a representation unit of an object and its slots contain knowledge of the object. Each frame contains a type slot, which makes it possible to determine its Relationship with other frames. Other slots contain properties of the frames, background information (reference), data etc.
...
The term Taxonomy has been borrowed from biology and describes the hierarchy of life on earth. In Quaestor a Taxonomy is a hierarchic structure of Entities (see also [wikipedia]).
An Entity is a Quaestor object that contains parameters that are either input, goal or to be computed with a particular relation. The relation can be a classic one or can be encapsulated in the Entity in which it is used. Any Entity contains at least a user defined name (QEntityName), a unique ID provided by Quaestor (QEntityId) and an index (QEntityIndex) in case of multiple instances. Any Entity may contain an image or (html) document providing additional explanation (QEntityDoc).
The Taxonomy and Entity use Quaestor s use Quaestor's capability to already deal with complex object data structures. A Taxonomy can be a generic description of an object (e.g. a ship structure) or a process (e.g. the design of a ship hull and/or the generation of a stability manual). So, a Taxonomy contains knowledge about the structure of a solution based on that Taxonomy. In a way the Taxonomy represents the DNA structure or blue print of the solutions that will be based on it.
...